Briefly Describe the Brain Changes That Occur in Adolescence.
Adolescent Brain Development. The main change is that unused connections in the thinking and processing part of your childs brain called the grey matter are pruned away.
Brain Development During Adolescence Lifespan Development
Increases efficiency improves memory IQ and READING not in PFC Interesting facts.

. In both boys n girls reproductive organs start producing spermshair growth on private areasboys start getting moustache facial hair. Changes like this are considered normal. Adolescence is a time of rapid cognitive development.
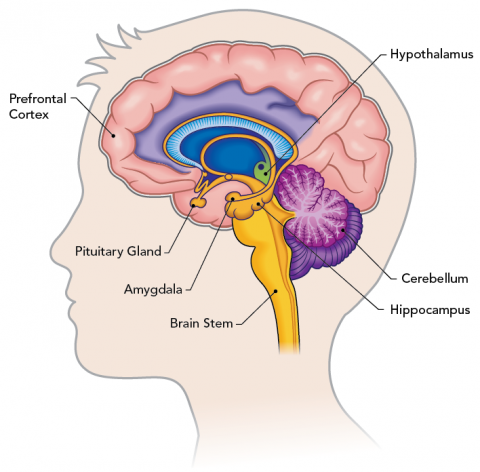
Changes in this part continue into early adulthood. Myelination and neurons increases significantly and gets impulses faster growth spurt a dramatic increase in height and weight that occurs during puberty primary sexual characteristics. Because the prefrontal cortex is still developing teenagers might rely on a part of the brain called the amygdala to make.
Click on the targets below to learn how the brain grows changes and adapts to its environment through. Tap card to see definition. 1 Brain volume DECREASES during adolescence.
These changes generally begin at puberty or shortly thereafter. Briefly describe the brain changes that occur in adolescence. USE IT OR LOSE IT.
Briefly describe the brain changes that occur in adolescence. Although it does not get larger it matures by becoming more interconnected and specialized Giedd 2015. The brain reaches 90 of its adult size by the time a person is six or seven years of age.
Growth and change are an integral part of adolescence. Different hormones produced and the body begins to change. Click again to see term.
A shifts in activity from the limbic system to the prefrontal cortex b an increase in myelination of the frontal cortex c remodeling pruning of synaptic connection and. 3 GIRLS brains are SMALLER but reach their maximum volume EARLIER. Thus the brain does not grow in size much during adolescence.
However when there is trauma divorce and abuse brain development changes. Biological changes in brain structure and connectivity in the brain interact with increased experience knowledge and changing social demands to produce rapid cognitive growth. There are dramatic changes in neural circuits particularly in frontal cortical and basal ganglia circuits during adolescence.
People often deride the function of the frontal cortex in teenagers. Studies on the brain during the last decade show that it -- along with height weight and hormones --goes through dramatic changes during the middle school years. Between the ages of 10 and 25 the brain undergoes changes that have important implications for behavior.
- Neurons continue to become myelinated and after a period of overabundance of synapses the number of synapses declines. Brain cells their connections and receptors for chemical messengers called neurotransmitters peak during childhood then decline in adolescence. To get under the hood scientists need to go back to the brains infancy and explore how it develops.
2 brain morphology is tied to HEREDITY more than environmental factors. At the same time other connections are strengthened. Briefly describe the brain changes that occur in adolescence.
During adolescence brain cells continue to bloom in the frontal region. However the creases in the brain continue to become more complex until the late teens. These qualities would help the teenager make sounder decisions in a responsible job like that of babysitting young children.
The corpus collusum thicken throughout adolescence which increases reaction times. The brain undergoes dramatic changes during adolescence. Inside the teenage brain Adolescence is a time of significant growth and development inside the teenage brain.
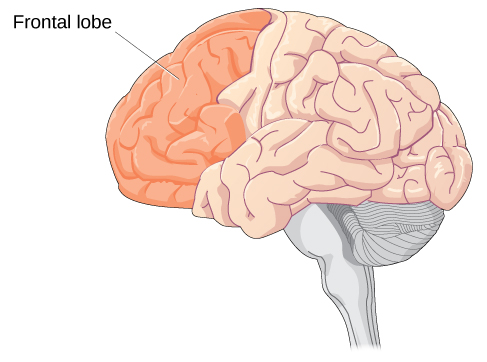
In rodents and primates this pathway undergoes extensive changes during adolescence. But unlike a static mechanical machine like a car or a dishwasher the brain is an organ that grows changes and learns. The three most important changes are in the corpus collosum amygdala and prefrontal cortex.
However this growth takes time and the growth is uneven. Brain Changes during Adolescence. With the maturation of the prefrontal cortex teenagers think with greater maturity responsibility and intelligence than ten or eleven year olds.
What are the three most important structural changes in the brain during adolescence. During adolescence myelination and synaptic pruning in the prefrontal cortex increase s improving the efficiency of information processing and neural connections between the prefrontal cortex and other regions of the brain are strengthened. Differentiate the three theories of intelligence.
The myelination and development of connections between neurons continues. While outward changes are easy to see brain development goes much deeper but it can go far in. The amygdala which regulates emotions and moods also develops.
For girls chest grow. With task-dependent oscillations the precision of synchronization of oscillatory activity in the theta alpha and beta bands increases. Throughout many changes they move into physical mental maturity and different emotions Cromer 2011.
Brain development in adolescence is associated with a decline of oscillatory activity at rest in the delta 03 Hz and theta 47 Hz bands and an increase in the alpha 812 Hz and beta bands 1330 Hz. We believe that these changes adjust and tune the brain in order to sculpt learning and decision-making at these different life stages. Some of the most developmentally significant changes in the brain occur in the prefrontal cortex which is involved in decision making and cognitive control as well as other higher cognitive functions.
Changes - Most brain changes during adolescence occur in the frontal regions. One of the most striking changes is the steady linear increase in dopaminergic neural projections that happens in both males and females in the brain area known as the medial prefrontal cortex or mPFC. During adolescence years the brain hasnt developed fully.
During adolescence myelination and synaptic pruning in the.

Adolescent Development Youth Gov

Brain Development During Adolescence Lifespan Development
No comments for "Briefly Describe the Brain Changes That Occur in Adolescence."
Post a Comment